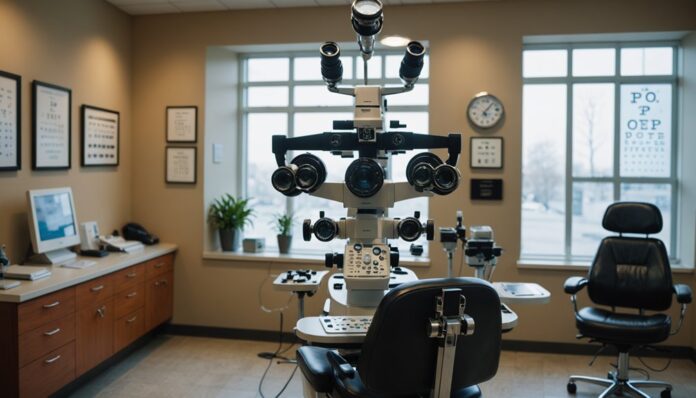
A routine eye exam is a thorough assessment of one’s vision and overall eye health. It begins with paperwork, where patients provide their medical history and insurance information. Next, visual acuity tests, typically using a Snellen chart, measure the sharpness and clarity of their vision. But what follows is a more detailed examination, designed to identify any underlying issues that may be affecting their sight, and potentially, their overall well-being.
Highlights
- Administrative tasks are completed before the exam, including paperwork, medical history, and insurance verification.
- Initial visual acuity tests, such as reading the Snellen chart, assess visual clarity and distance perception.
- Refraction tests determine the precise prescription for corrective lenses using a phoropter or autorefractor.
- A thorough eye health examination inspects the eyes, including eyelids, cornea, lens, retina, and optic nerve, for signs of eye diseases.
- Additional diagnostic tests, like glaucoma testing and retinal imaging, may be performed as needed for personalized care and treatment.
Pre-Exam Preparation and Paperwork
Before the eye exam begins, several administrative tasks must be completed to guarantee a smooth and efficient visit.
The pre-exam checklist involves gathering relevant medical history, verifying insurance coverage, and completing necessary paperwork. Patients are typically required to fill out a brief questionnaire detailing their medical history, allergies, and any previous eye problems.
Additionally, they may be asked to provide identification and insurance cards to confirm coverage. The completed paperwork is then reviewed by the eye care professional to identify any potential concerns or areas of focus for the exam.
Initial Visual Acuity Tests
Upon entering the examination room, patients are typically greeted by an eye care professional who begins the eye exam with a series of initial visual acuity tests.
These tests are designed to assess the patient’s visual clarity and distance perception. The most common visual acuity test is the Snellen chart, which consists of rows of increasingly smaller letters that the patient must identify from a distance of 20 feet.
This test helps the eye care professional determine the patient’s level of visual acuity and detect any potential vision problems. The results of this test serve as a baseline for the rest of the examination and provide significant information for making a diagnosis and recommending treatment.
The test is usually performed on both eyes, one at a time.
Refraction Tests for Corrective Lenses
While initial visual acuity tests provide a general idea of a patient’s visual clarity and distance perception, refraction tests are used to determine the exact prescription for corrective lenses.
A phoropter or an autorefractor are commonly used to perform refraction tests. These devices use different refraction methods to assess how well a patient’s eyes focus light and determine the appropriate lens prescriptions.
During the test, the patient is asked to look through the phoropter or autorefractor and identify which lenses provide the clearest vision. The results of the refraction test are then used to determine the patient’s precise prescription, including the correct spherical, cylindrical, and axis values for their corrective lenses.
Accurate refraction tests guarantee ideal lens prescriptions for patients, enhancing their overall vision and eye comfort.
Eye Health Examination and Screening
Conducting a thorough eye health examination and screening is an essential part of a routine eye exam. This assessment enables eye care professionals to detect potential eye diseases and vision changes that may be asymptomatic in their early stages.
A detailed eye health examination typically involves a visual inspection of the eyes, including the eyelids, cornea, lens, retina, and optic nerve. The eye care professional will look for signs of eye disease, such as cataracts, glaucoma, or age-related macular degeneration.
They will also assess the eyes for any abnormalities, such as retinal tears or detachment. By identifying potential issues early, eye care professionals can provide timely treatment and prevention strategies to help maintain ideal eye health and prevent vision loss.
Additional Diagnostic Tests as Needed
To supplement the thorough eye health examination, eye care professionals may employ additional diagnostic tests as needed to gather more detailed information about the eyes.
These tests may include glaucoma testing, which assesses the pressure within the eye to detect the presence of glaucoma, a condition that can cause vision loss if left untreated.
Retinal imaging is another diagnostic tool that captures detailed images of the retina, allowing eye care professionals to evaluate the health of the retina and optic nerve.
These tests help identify potential issues and enable eye care professionals to provide personalized care and treatment recommendations.
Reviewing and Discussing Your Exam Results
Upon completion of the eye exam and any additional diagnostic tests, eye care professionals thoroughly review the results to assess the overall health of the patient’s eyes.
This review process involves analyzing the exam findings to identify any potential vision problems or eye diseases. The eye care professional will then discuss the results with the patient, explaining their findings in a clear and concise manner.
If any issues are detected, the eye care professional will outline treatment options and make recommendations for the best course of action.
This discussion is an essential part of the eye exam process, as it enables patients to make informed decisions about their eye health and take proactive steps to protect their vision.
Conclusion
A routine eye exam is an extensive assessment of one’s vision and eye health. Through a series of tests, including visual acuity and refraction assessments, eye care professionals evaluate and address vision needs. A detailed examination of eye health, supplemented by additional diagnostic tests as needed, guarantees that any potential issues are identified and treated. The exam concludes with a review of results, providing individuals with a clear understanding of their eye health and any necessary next steps.